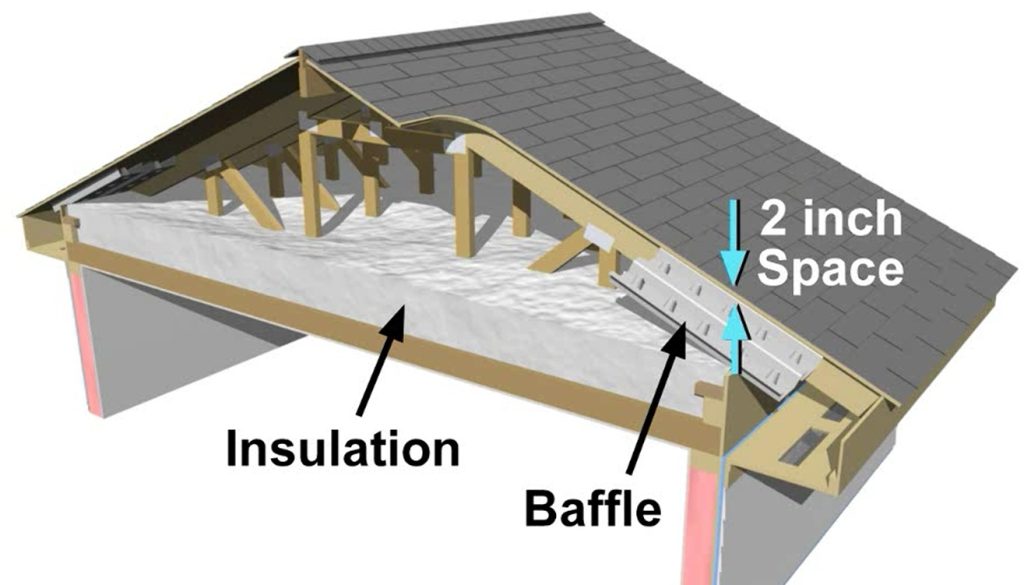
When it comes to maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home, one of the most important elements to consider is insulation. Proper insulation helps keep your home warm in the winter and cool in the summer, leading to a more stable indoor temperature and lower energy costs. One of the most common insulation ratings used for ceilings is R 30 ceiling insulation. This article explores what R 30 ceiling insulation is, why it is important, and how you can install it to optimize your home’s comfort and energy efficiency.

What is R 30 Ceiling Insulation?
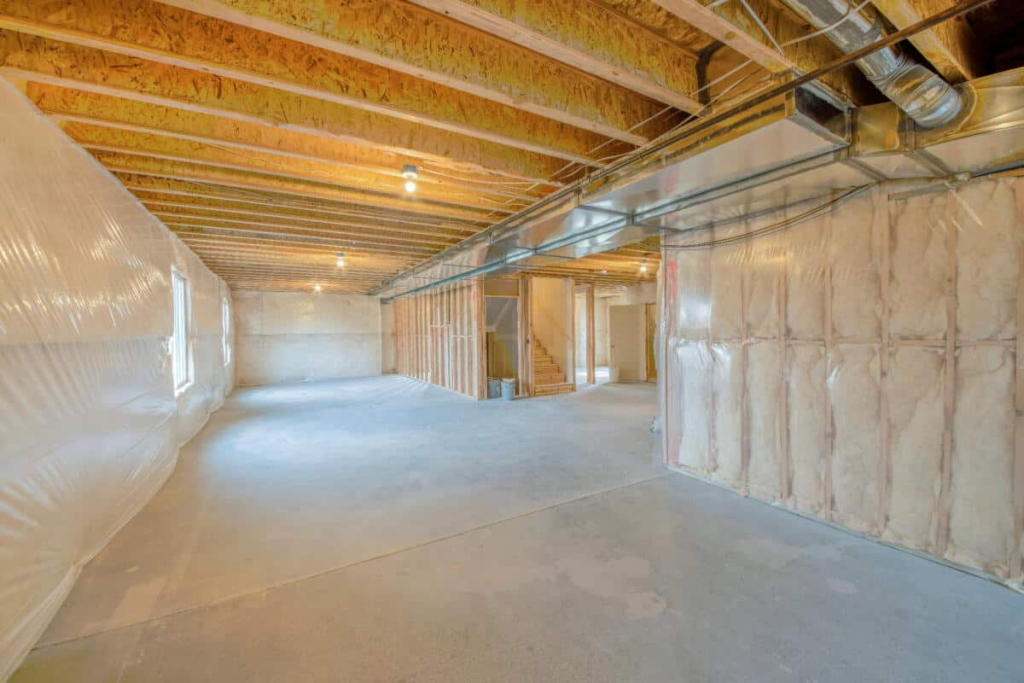
R 30 ceiling insulation refers to the insulation material that has an R-value of 30. The R-value is a measure of an insulation material’s ability to resist heat flow, with higher values indicating greater insulating power. Essentially, R 30 insulation provides a level of resistance to heat transfer that is ideal for ceilings in climates with moderate to cold temperatures.
The R 30 rating is commonly used in areas like attics, ceilings, and roofs, where maintaining a consistent indoor temperature is essential. This level of insulation is ideal for homes located in regions that experience cold winters or areas where homeowners want to reduce their heating and cooling costs significantly. The insulation’s primary function is to prevent heat from escaping in the winter and to block heat from entering during the hot summer months.
Read too: Shiplap Ceiling in Kitchen: A Timeless Trend for a Stylish and Cozy Space
Why Choose R 30 Ceiling Insulation for Your Home?
R 30 ceiling insulation offers numerous benefits, particularly for homeowners looking to improve energy efficiency and comfort. Below are some reasons why you might want to consider adding this insulation to your home.
1. Energy Efficiency
The primary benefit of R 30 ceiling insulation is its energy efficiency. Insulation works by trapping air in pockets, which reduces the amount of heat that can pass through. This helps keep your home warm in winter and cool in summer, reducing the need for heating and air conditioning. With R 30 ceiling insulation, you’ll notice a decrease in your energy bills as your HVAC system works less to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
In fact, studies show that up to 40% of a home’s energy loss occurs through the attic. By properly insulating your ceiling with an R 30-rated material, you can significantly reduce this heat loss and improve the overall energy efficiency of your home.
2. Enhanced Comfort
Proper ceiling insulation helps to maintain a more stable indoor temperature throughout your home. With R 30 ceiling insulation, you will experience less fluctuation in temperature, keeping rooms warmer during winter and cooler in the summer. This increased comfort can make a significant difference in your living experience, especially in areas that see extreme temperature changes.
Additionally, insulation helps reduce drafts and cold spots in your home, particularly in rooms located directly under the roof or attic.
3. Soundproofing
In addition to temperature control, R 30 ceiling insulation can also serve as a sound barrier. Insulation materials like fiberglass, cellulose, or spray foam can help reduce sound transmission between rooms and floors. This can be particularly useful in homes with multiple levels or in apartments and townhouses where soundproofing is often a concern.
4. Increased Home Value
A well-insulated home is a valuable asset, as potential buyers will appreciate the energy savings and comfort that come with an effectively insulated home. By installing R 30 ceiling insulation, you’re not only improving your home’s energy efficiency but also increasing its market value.
In many regions, homes with higher R-value insulation are seen as more desirable due to the long-term savings they offer in terms of utility bills. If you’re planning to sell your home in the future, adding insulation can make it more attractive to buyers.
Different Types of R 30 Ceiling Insulation
There are several types of insulation materials available that provide an R 30 rating. The best material for your home depends on your budget, climate, and specific needs. Below are some of the most common types of insulation used for R 30 ceiling insulation:
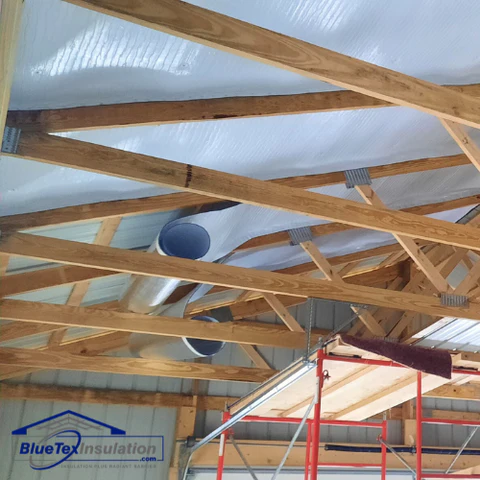
1. Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass is one of the most widely used materials for ceiling insulation. It is cost-effective, readily available, and easy to install. Fiberglass insulation can come in batts (pre-cut rolls) or loose-fill form, and it is often the go-to choice for attics and ceilings.
Fiberglass batt insulation is typically used for standard ceiling sizes, and it provides an excellent balance of R-value and cost. It’s also non-combustible and resistant to moisture, making it ideal for areas with varying humidity levels.
2. Cellulose Insulation
Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper products and is often used in attics and ceilings. It is blown into place, which allows for a more complete fill, reducing gaps or voids in the insulation. Cellulose has a higher R-value per inch than fiberglass, so fewer layers are needed to achieve the desired R-value.
This type of insulation is also environmentally friendly, making it an excellent option for eco-conscious homeowners.
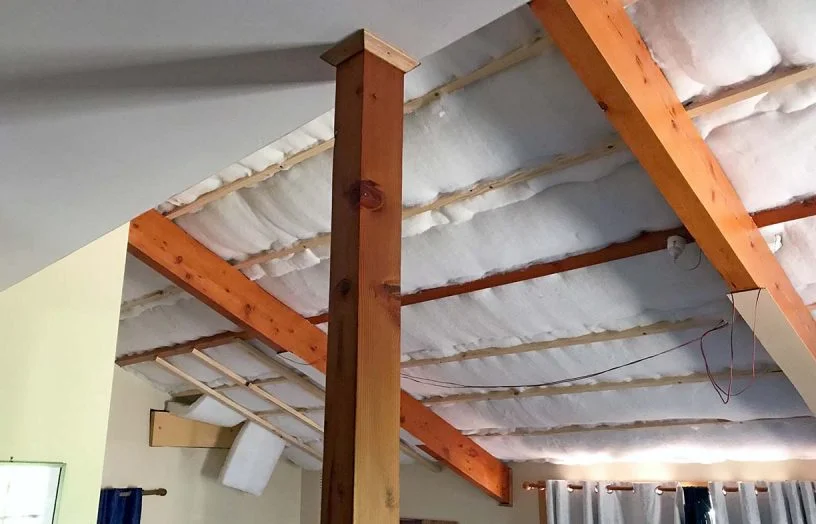
3. Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is a high-performance option that provides an airtight seal. It is sprayed directly onto the ceiling surface and expands as it dries, filling all cracks and gaps. Spray foam insulation provides a higher R-value per inch compared to fiberglass and cellulose, making it a good option for areas where space is limited or where you need superior performance.
Spray foam is particularly effective at preventing air leaks, which can result in significant energy loss. However, it is generally more expensive than fiberglass or cellulose insulation.
4. Cotton or Denim Insulation
For those looking for a sustainable and non-toxic option, cotton or denim insulation is an alternative worth considering. Made from recycled cotton fabric or denim, this material is safe to handle and has a relatively high R-value. While it is not as commonly used as fiberglass or cellulose, it can provide good performance for ceiling insulation.
Installation Tips
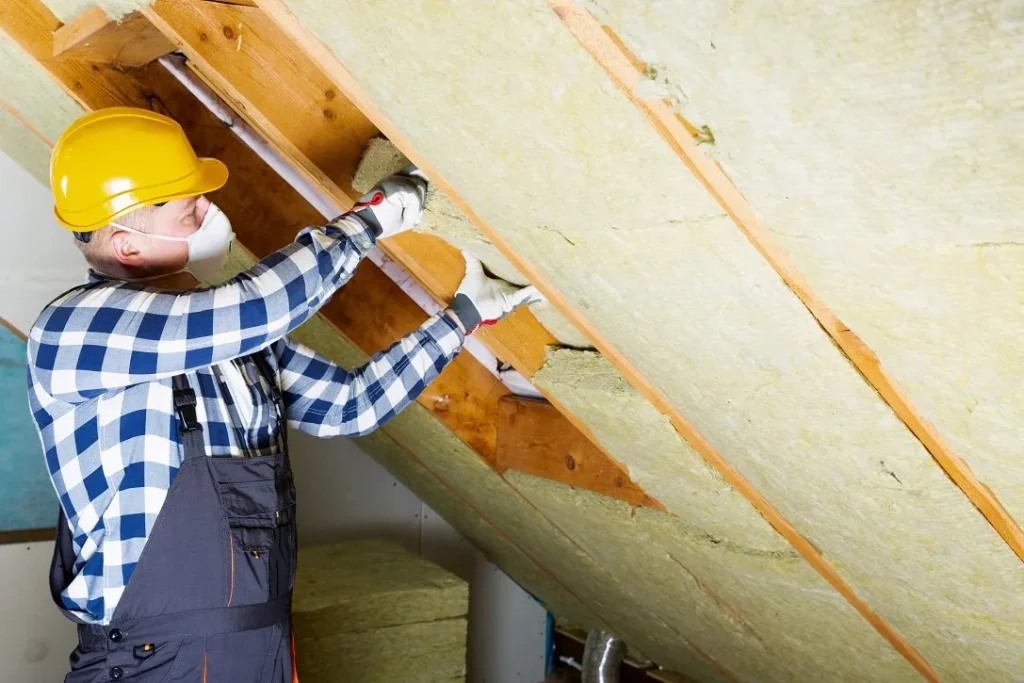
Installing R 30 ceiling insulation is a straightforward process, but it can require some preparation and effort. While it’s always a good idea to hire a professional for insulation installation, many homeowners can complete the task themselves if they have the right tools and follow safety guidelines. Here’s a basic guide to installing ceiling insulation:
1. Measure the Space
Start by measuring the area of the ceiling that needs to be insulated. This will help you determine how much insulation material you’ll need to buy. Be sure to account for the full area of the attic or ceiling, including any nooks or corners.
2. Choose the Right Insulation Material
Choose the insulation material that best suits your needs. If you’re working with a tight budget, fiberglass batt insulation may be the most cost-effective choice. If you’re looking for superior performance and soundproofing, spray foam might be the best option.
3. Install the Insulation
For batt insulation, lay the pieces between the ceiling joists, ensuring that they fit snugly. If using loose-fill insulation, you’ll need to use a blower to fill the area evenly. Spray foam insulation should be applied by a professional to ensure it’s done properly.
4. Seal Gaps and Joints
Ensure there are no gaps or spaces in the insulation material. Any gaps could lead to heat loss and reduced performance. Seal all joints and edges with tape or foam sealant to create an airtight barrier.
Conclusion
R 30 ceiling insulation is an excellent way to improve your home’s energy efficiency, comfort, and overall performance. By investing in high-quality insulation, you can reduce energy costs, maintain a comfortable indoor environment, and increase the value of your home. Whether you choose fiberglass, cellulose, spray foam, or another material, ensure that your insulation is properly installed for maximum effectiveness.