Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can occur in people with diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes. Experiencing DKA can be frightening and overwhelming, but understanding what it is, what causes it, and how to manage it can help individuals better navigate this challenge. This article delves into the DKA experience, offering insights into its symptoms, triggers, and treatment options while sharing tips for prevention and care.
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
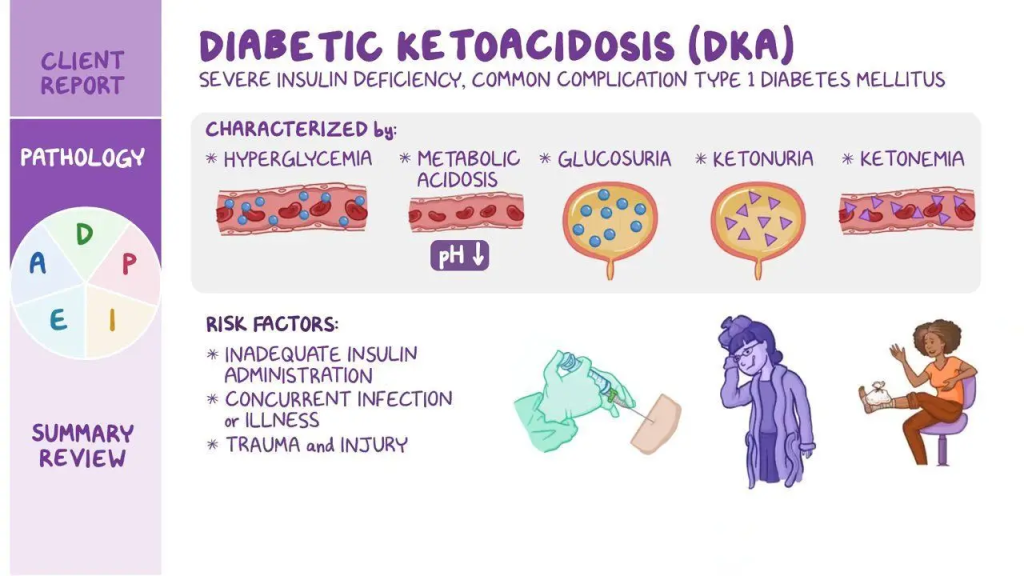
Before exploring the DKA experience, it is essential to understand what DKA is. Diabetic Ketoacidosis occurs when the body lacks enough insulin to process glucose for energy. In response, the body starts breaking down fats for fuel, leading to the production of ketones. When ketones build up in the bloodstream, they cause the blood to become acidic, resulting in DKA.
Read too: What is Diabetic Profile Test? A Complete Guide to Understanding Its Importance and Procedure
DKA is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including organ damage, coma, or even death. While DKA is more common in people with type 1 diabetes, it can also occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes under certain circumstances.
Signs and Symptoms of a DKA Experience
Recognizing the symptoms of DKA is crucial for timely intervention. Based on accounts from individuals who have had a DKA experience, the condition often develops rapidly, with the following symptoms:
- Excessive Thirst and Frequent Urination: The body tries to eliminate excess ketones and glucose through urine, leading to dehydration.
- Fatigue and Weakness: The lack of glucose energy and dehydration can result in severe exhaustion.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many people with DKA report persistent nausea and vomiting, worsening dehydration and acid imbalance.
- Abdominal Pain: This symptom is frequently described in DKA experiences, often accompanied by general discomfort.
- Fruity-Smelling Breath: The presence of ketones in the bloodstream can lead to a sweet or fruity odor on the breath.
- Rapid Breathing or Shortness of Breath: This occurs as the body attempts to compensate for the blood’s acidic pH levels.
- Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating: Severe cases of DKA can impair cognitive function due to the impact on brain activity.
If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
DKA Experience – Triggers and Risk Factors
Understanding what can lead to DKA is a critical part of managing diabetes. Many individuals who share their DKA experiences identify specific triggers that contributed to the condition.
1. Missing Insulin Doses
One of the most common causes of DKA is insufficient insulin. Forgetting or skipping insulin doses can leave the body unable to process glucose, leading to ketone production.
2. Illness or Infection
Illnesses, such as the flu or infections, can increase the body’s demand for insulin. During such times, the risk of DKA rises, as glucose levels may spike unexpectedly.
3. New Diagnosis of Diabetes
For some, their first DKA experience occurs before being diagnosed with diabetes. Without proper treatment, blood sugar levels and ketone production can escalate.
4. Physical or Emotional Stress
Stress, whether physical (e.g., surgery, trauma) or emotional, can trigger hormonal changes that elevate blood sugar levels. This can be a contributing factor to a DKA experience.
5. Alcohol or Drug Use
Certain substances, including alcohol and recreational drugs, can interfere with insulin effectiveness and blood sugar control, heightening the risk of DKA.
Treatment for DKA: What to Expect During a DKA Experience
A significant part of managing a DKA experience involves understanding how it is treated. Medical professionals typically address DKA using a multi-pronged approach to stabilize the patient and restore balance.
1. Rehydration
Since dehydration is a hallmark of DKA, intravenous (IV) fluids are administered to replenish lost fluids and electrolytes. This helps dilute excess glucose and ketones in the blood.
2. Insulin Therapy
Insulin is given through an IV to reduce blood sugar levels and halt ketone production. Patients with a DKA experience often describe rapid improvement once their insulin levels are restored.
3. Electrolyte Replacement
DKA disrupts the balance of electrolytes, such as potassium, sodium, and chloride. Replenishing these electrolytes is vital for maintaining proper bodily functions.
4. Monitoring and Ongoing Care
During and after a DKA experience, close monitoring of blood sugar, ketone levels, and overall health is essential to ensure recovery and prevent recurrence.
Preventing DKA: Learning from Experiences
For those who have gone through a DKA experience, prevention becomes a top priority. The following strategies can help individuals with diabetes avoid future episodes of DKA:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar and Ketone Levels
Regularly checking blood sugar levels and using ketone test strips during illness or high blood sugar episodes can provide early warnings of DKA.
2. Follow Your Insulin Regimen
Adhering to your prescribed insulin dosage and schedule is one of the most effective ways to prevent DKA. Discuss any adjustments with your healthcare provider if your routine changes.
3. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration helps flush out excess glucose and ketones, reducing the risk of dehydration-related complications.
4. Plan for Sick Days
Work with your healthcare team to develop a sick-day plan that includes insulin adjustments, ketone testing, and hydration strategies to manage blood sugar levels during illness.
5. Seek Support
Many individuals find that sharing their DKA experiences in support groups or online communities provides valuable emotional support and practical tips for managing diabetes.
Living with Diabetes After a DKA Experience
A DKA experience can be a turning point for many individuals, prompting them to take their diabetes management more seriously. By learning from the experience and implementing effective strategies, many people with diabetes go on to live healthier, more balanced lives.
1. Strengthening the Support Network
Having a support system, including healthcare providers, family, and friends, can make a significant difference in managing diabetes and preventing DKA.
2. Leveraging Technology
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps are technological advancements that can help individuals keep a closer eye on their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of future DKA.
3. Educating Yourself and Others
Understanding diabetes and sharing information about DKA with loved ones can create a safer environment where everyone knows how to recognize and respond to symptoms.
Conclusion: Learning from a DKA Experience
A DKA experience can be an overwhelming and challenging event, but it is also an opportunity to reflect, learn, and improve diabetes management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to prevent DKA and maintain better overall health.
Whether it’s through diligent blood sugar monitoring, consistent insulin use, or connecting with others who have faced similar challenges, managing diabetes after a DKA experience is achievable with the right tools and support.

Leave a Reply